As Large Language Models (LLMs) become more common in SaaS products and enterprise systems, one challenge keeps surfacing: accuracy.
LLMs are powerful, but they do not inherently “know” your business data. Left on their own, they generate responses based on training data and probability – not on your internal knowledge, documents, or real-time information.
This is where Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) becomes critical.
RAG is not just another AI buzzword. It is a practical architecture pattern that makes AI systems more accurate, explainable, secure, and useful in real-world products.
This blog explains what RAG is, how it works, real-world use cases, and why it has become the preferred approach for production-grade AI systems.
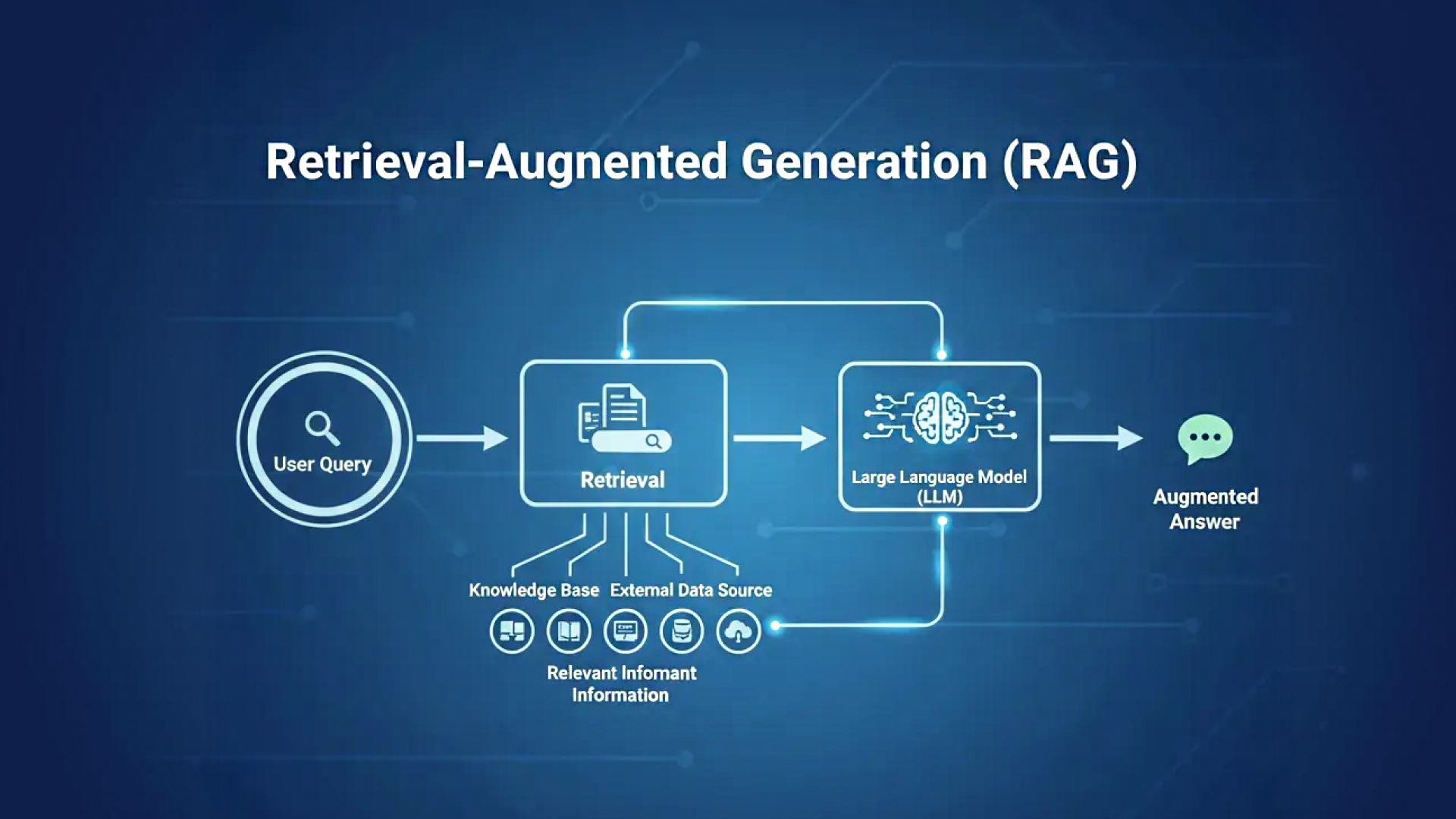
What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI architecture that combines two components:
- Retrieval – Fetching relevant information from trusted data sources
- Generation – Using an LLM to generate responses based on the retrieved data
Instead of asking an LLM to answer from memory alone, RAG ensures the model responds grounded in your actual data.
In simple terms:
RAG allows an LLM to “look things up” before answering.
This dramatically improves correctness and trustworthiness.
Why Pure LLMs Are Not Enough for Real Products
Out-of-the-box LLMs have limitations:
- They hallucinate confidently
- They cannot access private or proprietary data
- Their training data is static and outdated
- They struggle with domain-specific accuracy
- They cannot cite sources reliably
For consumer chatbots, this may be acceptable.
For SaaS, enterprise, fintech, healthcare, or internal systems, it is not.
RAG solves these problems by anchoring AI responses to real, verifiable data.
How RAG Works
A typical RAG pipeline looks like this:
Step 1: Data Preparation
Your trusted data sources are collected and indexed:
- Product documentation
- Knowledge bases
- PDFs and contracts
- Support tickets
- Databases
- Internal wikis
The data is chunked and converted into vector embeddings.
Step 2: Retrieval
When a user asks a question:
- The query is converted into an embedding
- A vector search retrieves the most relevant content chunks
- Only the most contextually relevant data is selected
This step ensures precision.
Step 3: Augmented Prompting
The retrieved content is injected into the LLM prompt as context.
The model is instructed:
- “Answer using only the provided information.”
- “If the answer is not found, say s.o”
Step 4: Generation
The LLM generates a response grounded in retrieved data – not guesses.
This is what makes RAG reliable, explainable, and production-ready.
Why RAG Adds Real Business Value
RAG is not about making AI smarter – it’s about making AI useful and safe.
Key Benefits
- Dramatically reduces hallucinations
- Improves factual accuracy
- Enables AI over private data
- Keeps data up to date without retraining models
- Improves user trust
- Supports compliance and governance
This is why most serious AI products today rely on RAG.
Real-World Use Cases of RAG
1. AI-Powered Knowledge Assistants
Employees or users can ask questions like:
- “How does our refund policy work?”
- “What were the key issues in last month’s incidents?”
- “Summarize this document for me.”
RAG ensures answers come from official sources, not assumptions.
2. Customer Support Automation
Instead of generic chatbots:
- RAG bots answer using help docs and ticket history
- Responses are consistent and accurate
- Support teams get AI-generated drafts grounded in facts
This reduces resolution time without risking misinformation.
3. SaaS In-Product Help
Users ask contextual questions inside the product:
- “How do I configure this feature?”
- “Why is this metric changing?”
RAG connects the UI context with internal documentation.
4. Compliance & Policy Assistants
In regulated industries:
- AI answers must be traceable
- Responses must align with official policies
RAG ensures AI only uses approved documents.
5. Internal Search and Documentation
RAG replaces poor internal search with:
- Semantic understanding
- Natural language queries
- Accurate summaries
This improves productivity across engineering, sales, and operations.
RAG vs Fine-Tuning: What’s the Difference?
| Aspect | RAG | Fine-Tuning |
| Uses private data | Yes | No (directly) |
| Data freshness | Real-time | Static |
| Hallucination risk | Low | Medium |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Easier | Complex |
| Compliance | Strong | Risky |
Key insight:
Fine-tuning changes how a model speaks.
RAG changes what a model knows.
For most SaaS and enterprise use cases, RAG is the better first choice.
Architecture Considerations for RAG Systems
RAG is powerful – but only when designed correctly.
Key Design Considerations
- Data quality and chunking strategy
- Embedding model selection
- Vector database choice
- Retrieval accuracy (top-k tuning)
- Prompt design and constraints
- Latency and cost control
- Security and access control
Poor RAG design leads to:
- Irrelevant answers
- High costs
- Slow response times
Rezolut focuses heavily on retrieval quality and prompt discipline, which are the real success factors.
Common Mistakes Teams Make with RAG
- Indexing everything without curation
- Poor chunking that loses context
- Treating RAG as “plug and play.”
- Not validating responses
- Ignoring observability and logging
- Allowing AI to answer outside the retrieved data
RAG systems need engineering rigor, not just API calls.
Security and Governance with RAG
One of RAG’s biggest strengths is data control.
With proper design:
- Sensitive data never leaves your system
- Access control limits what AI can retrieve
- Audit logs track AI usage
- Outputs can be traced to sources
This makes RAG suitable for:
- FinTech
- InsurTech
- Healthcare
- Enterprise SaaS
Rezolut implements RAG with security-first defaults, especially for regulated environments.
When You Should Use RAG (and When You Shouldn’t)
Use RAG When:
- Answers must be accurate
- Data is private or proprietary
- Information changes frequently
- Compliance matters
- Trust is critical
Avoid RAG When:
- The task is purely creative
- No factual grounding is required
- Latency must be near zero
- Deterministic logic is better
RAG is a tool – not a default for every AI problem.
Conclusion
Retrieval-Augmented Generation is not hype – it is the backbone of trustworthy AI systems.
RAG transforms LLMs from impressive demos into reliable, enterprise-ready components by grounding responses in real data. It reduces hallucinations, improves trust, and enables AI adoption in environments where accuracy matters.
For SaaS companies and startups, RAG is often the difference between:
- An AI feature users tolerate
- And an AI capability that users rely on
With the right architecture and execution partner, RAG becomes a long-term competitive advantage – not just an experiment.